Digital Psychrometer: Climate Control, Quality Protection – The Vital Importance of Calibration

In most industrial and controlled settings, Temperature (T) and Humidity (RH) are vital. These factors decide product quality, equipment performance, and human safety. Even small climate control errors can cause major material losses. For example, sensitive product failures or building mold can result. The Digital Psychrometer is an essential tool. It gives accurate readings for temperature, relative humidity (RH), Dew Point, and Wet Bulb temperature. Therefore, HVAC/R experts and safety staff can make correct system decisions. However, humidity sensors (often polymer-based) are prone to dirt, chemicals, and age. This means they are likely to drift. Thus, routine Digital Psychrometer Calibration is mandatory. Calibration checks the sensor’s accuracy. In short, it keeps the environment tightly controlled to meet standards.
1. What is a Digital Psychrometer? Core Functionality

1.1. Critical Measurement Parameters
Digital psychrometers go beyond basic measurements, providing key indicators of the air’s thermodynamic state used for condensation control, HVAC optimization and safety.
Dry Bulb Temperature (T)
Direct measurement. Usually Thermistor/RTD.
Relative Humidity (RH)
Direct measurement. Capacitive or resistive sensor.
Dew Point (Tdp)
Derived calculation. Condensation risk assessment.
Wet Bulb Temperature (Twb)
Derived calculation. Evaporative cooling / Heat stress safety.
This device offers key calculated values. Furthermore, it is much more useful than a standard thermometer.
-
Relative Humidity (RH): This is the percentage of water vapor present. It is compared to the maximum amount the air can hold.
-
Dew Point: This is the temperature where water vapor starts to become liquid. Therefore, it is vital for stopping condensation on surfaces like metal or electronics.
-
Wet Bulb Temperature: This is the air temperature after full adiabatic cooling. Notably, this value is key for HVAC calculations and workplace heat safety.
-
Dry Bulb Temperature: This is the usual ambient air temperature.
2. Vital Applications in Industrial and Controlled Environments
Criticality Analysis of Derived Climate Data
While T and RH are primary data, mission-critical applications often rely on Dew Point (Tdp) and Wet Bulb (Twb). Tdp is key for condensation control (semiconductors, coatings), while Twb is vital for HVAC performance and heat-stress safety.
- Tdp: crucial for industries requiring strict condensation control.
- Twb: essential for thermal comfort, evaporative cooling and heat safety.
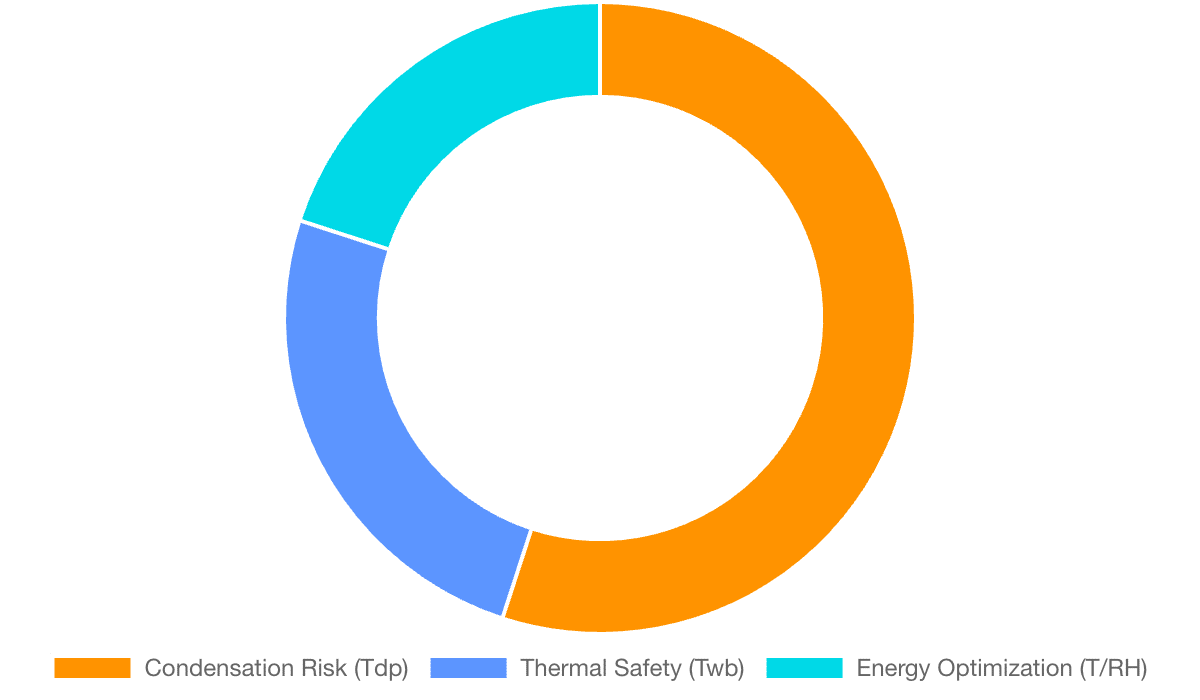
Accurate T/RH control directly affects both quality and safety.
2.1. Product Quality Control
-
Electronics & Semiconductors: High humidity causes shorts or rust. Conversely, low humidity can create electrostatic discharge (ESD). Accurate measurement keeps ideal conditions.
-
Pharmaceuticals & Food: T/RH control is required in storage and production. This prevents spoilage and ensures a long product shelf life.
2.2. Occupational Safety and Facilities Management
-
Heat Stress Assessment: Wet Bulb temperature measurement helps find the heat stress index. Thus, it protects workers in hot environments.
-
Mold Prevention: It helps staff find high Dew Point areas. In these areas, the risk of condensation and mold growth is highest. Mold harms building structure and health.
2.3. HVAC Systems
2.4. Clean Rooms
3. The Absolute Role of Digital Psychrometer Calibration
Simulated RH Sensor Drift Over Time
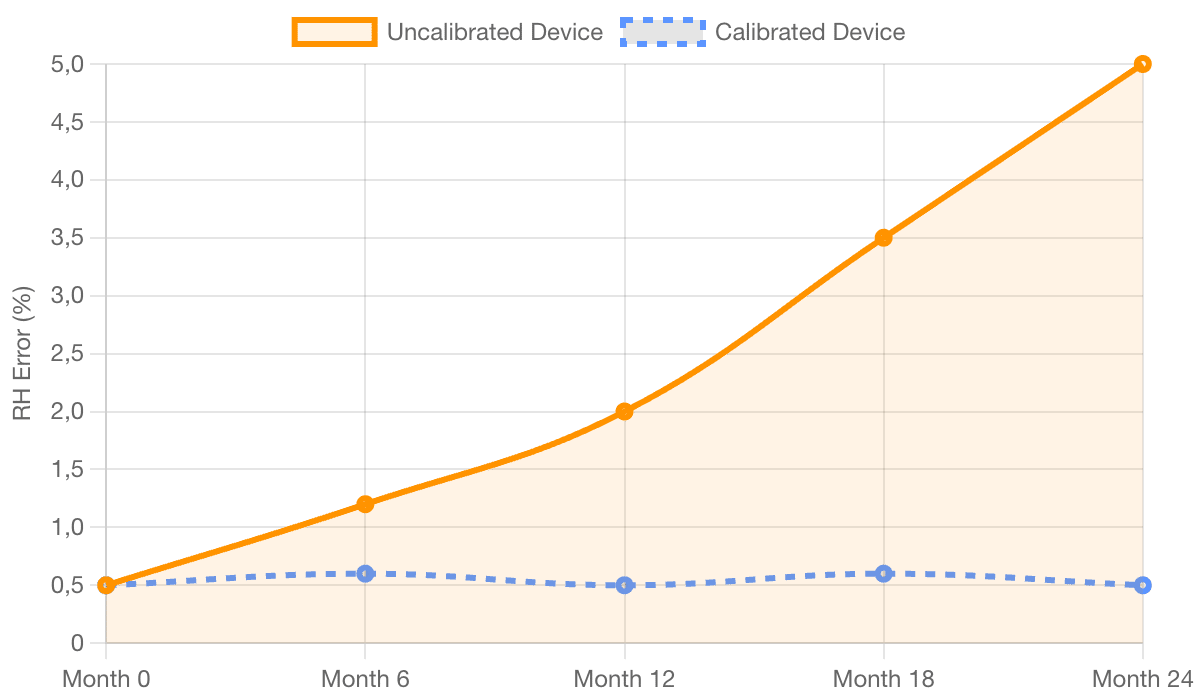
Sensor accuracy is vital. A wrong humidity reading can cause faulty system changes. This results in wasted energy or damaged products.
3.1. Protecting Accuracy and Preventing Drift
-
Vulnerable Sensors: Humidity sensors (capacitive or resistive) are prone to chemical “poisoning.” Dirt or natural aging also cause them to report wrong humidity.
-
Calibration Verification: Calibration checks the sensor’s reaction. Specifically, it confirms that the sensor correctly reads traceable T/RH standards.
-
HVAC Optimization: Calibration confirms the HVAC system’s input data is correct. Therefore, the system runs at peak energy efficiency. It also prevents unnecessary strain.
3.2. Compliance with International Standards and Audits
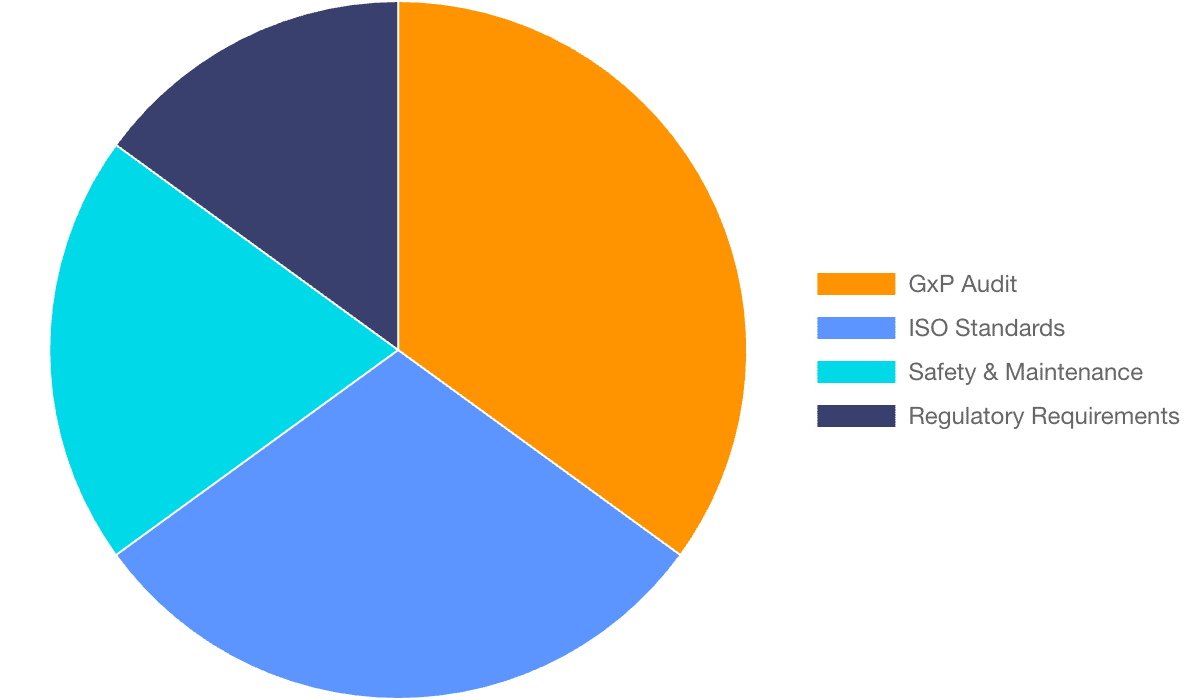
-
GxP/ISO Requirements: Strict rules like GMP and GLP require periodic Traceable Calibration. Furthermore, ISO standards like ISO 9001 also mandate this.
-
Valid Evidence: The Calibration Certificate gives solid proof. It shows that controlled conditions are valid and meet legal rules. Ultimately, this is crucial for FDA or other regulatory audits.
4. Digital Psychrometer Calibration Process
Periodic calibration restores sensor accuracy and establishes traceability in accordance with ISO/IEC 17025.
Reference Standard
Use calibrated humidity/temperature chambers or saturated-salt references.
Test & Comparison
Compare device readings at multiple known T/RH points.
Adjustment & Correction
Adjust response curve or apply correction factors if required.
Certification (ISO/IEC 17025)
Issue calibration certificate as evidence of traceability and compliance.
The calibration process is done by experts. This ensures the sensor’s reliability.
-
Reference Standards: First, traceable and calibrated T/RH standards are used. For instance, they use humidity generators or saturated salt solutions.
-
Test and Comparison: Next, a technician puts the device in known T/RH conditions. They compare the psychrometer’s reading with the exact value from the standard. This is done across many points.
-
Adjustment and Confirmation: If the error is too large, the device is adjusted with software. Otherwise, correction factors are applied. This ensures correct operation.
-
Certification: Finally, a Calibration Certificate is issued. This paper confirms the accuracy, uncertainty, and the next due date.
Conclusion
The Digital Psychrometer protects the working environment, product quality, and overall operational productivity. However, its true value depends entirely on the accuracy and stability of its sensors. For this reason, routine Digital Psychrometer Calibration is not optional – it is mandatory. This process prevents measurement drift, corrects hidden errors, and guarantees long-term reliability. Most importantly, it ensures that every climate-related decision is based on trusted data. In the long run, proper calibration reduces energy waste, protects sensitive products, prevents costly failures, and helps organizations comply with strict industry quality and regulatory requirements.



