The Gold Standard of Sterilization: Autoclave Applications and Why Calibration is Key
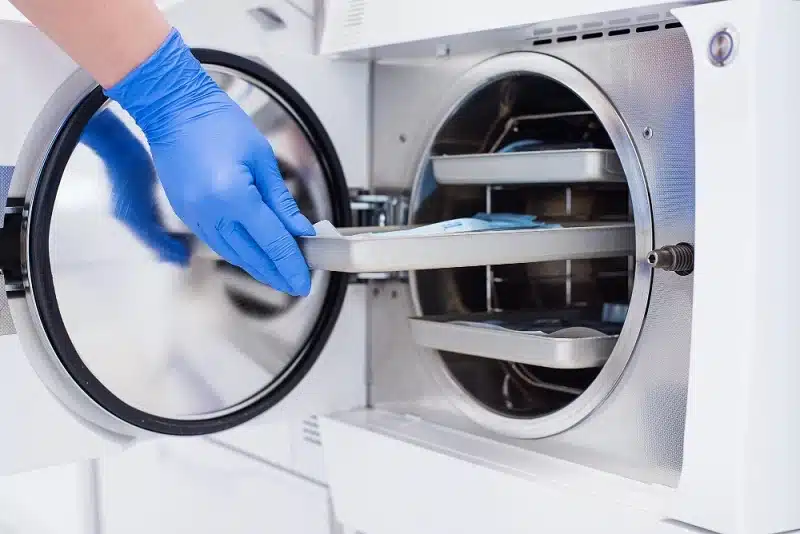

In the fields of medicine, pharmaceuticals, and biological science, sterility is the ultimate, non-negotiable requirement. Every single microorganism must be eliminated to safeguard patient safety and ensure the reliability of research outcomes. The workhorse that fulfills this critical mission is the Autoclave (Steam Sterilizer). The autoclave operates on a powerful yet straightforward principle: saturated steam under high pressure. This superheated, pressurized steam is uniquely effective at killing all microbial life, including bacterial spores—the most tenacious survivors. However, no matter how advanced the technology, an autoclave’s efficacy hinges entirely on the accuracy of its operational parameters. This is precisely where Autoclave Calibration steps in, acting as the final, crucial guardian of safety and quality.
1. Diverse Applications: Autoclaves Are Everywhere Sterility is Needed
The autoclave is more than just a hospital device; it supports every industry that requires high hygiene and infection control.
Core Applications (Mandatory Sterilization)
HEALTHCARE & MEDICAL
- ✨ Surgical Instruments
- ☣️ Biohazard Waste Disposal
- 🦷 Dental & Aesthetics
SCIENCE & RESEARCH
- 🌱 Culture Media Sterilization
- 🧪 Laboratory Equipment Sterility
- 🧬 Biology & Pharma R&D
INDUSTRY & OTHERS
- 💊 Pharmaceutical Manufacturing (GMP)
- 🥫 Canned Food Sterilization
- 💉 Tattooing (Equipment)
1.1. Core Applications in Healthcare and Patient Safety
Patient safety is the top concern. The autoclave ensures safety in all invasive procedures.
- Surgical Instrument Sterilization: This is the most critical use. Staff must sterilize all metal tools, reusable optical devices, and heat-resistant supplies before, during, and after surgery. For example, poor sterilization can lead to Surgical Site Infections (SSIs), which seriously endanger patients.
- Biohazardous Waste Disposal: Facilities use autoclaves to deactivate infectious biohazardous waste. This includes blood samples, culture tubes, contaminated sharps, and tissue. This process is essential for environmental rules and biological safety laws.
- Dental and Aesthetic Practices: All reusable instruments in dental clinics, aesthetic surgery centers, and even tattooing facilities must undergo steam sterilization. This prevents the spread of dangerous diseases like Hepatitis B, C, or HIV.
1.2. Essential Roles in Science and Research
The integrity of scientific results depends on a sterile lab environment.
- Culture Media Sterilization: Microbiology labs rely on autoclaves to sterilize liquid media (Broth) or solid media (Agar). Technicians use this sterilized media to grow bacteria, fungi, or cells. Contaminated media can easily spoil the research or diagnostic results.
- Lab Glassware Sterilization: Staff must sterilize test tubes, petri dishes, pipettes, and other glass supplies. This ensures no strange microorganisms interfere with experiments.
- Pharmaceutical and Biological Manufacturing: During the creation of vaccines, sterile injectable drugs, and biological products, autoclaves sterilize equipment, packaging, and sometimes the final product itself.
1.3. Applications in Industry and Other Sectors
Beyond the medical and research worlds, several industries rely on the autoclave’s power for quality control and public safety.
- Pharmaceutical Industry: Manufacturers use autoclaves to sterilize equipment and raw materials. This step is mandatory in the production of sterile drugs and injectable medicines.
- Food Industry: Businesses use autoclaves to sterilize certain test samples or processing equipment. This helps ensure food safety and validates testing procedures.
- Tattoo and Aesthetic Services: All reusable needles, tubes, and metal instruments must undergo sterilization. This protects clients from potential infections transmitted through contaminated tools.
2. The Critical Need for Autoclave Calibration
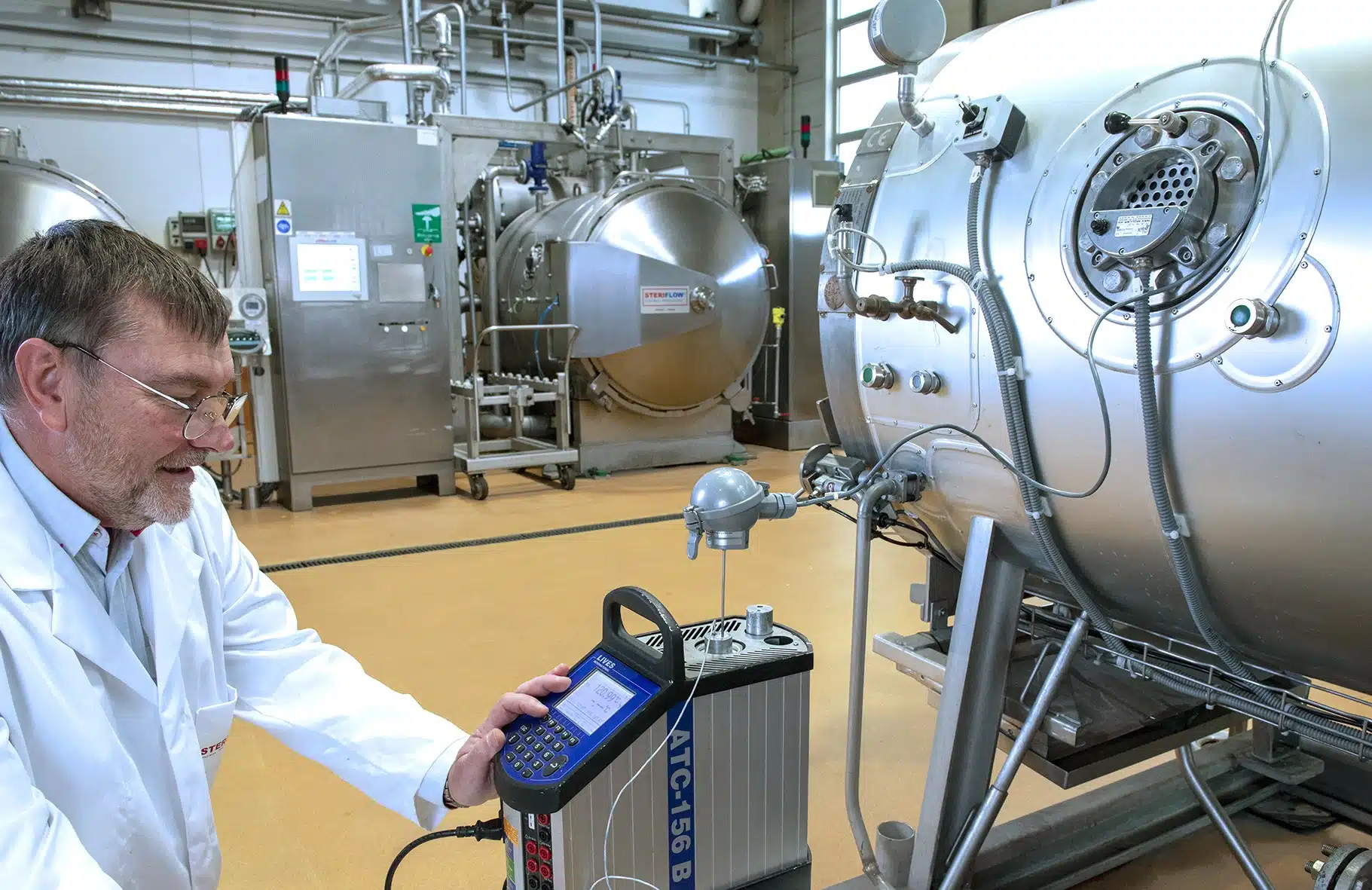

Why must businesses calibrate an autoclave often? Simply because sterilization success relies on three main physical facts: Temperature, Pressure, and Time at Hold.
Calibration: Why It Matters?
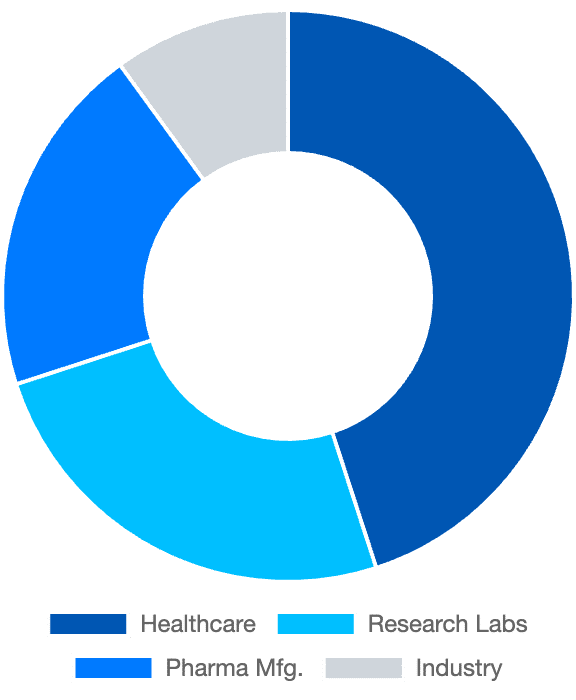
Autoclave Usage Distribution
Usage percentage by sector.
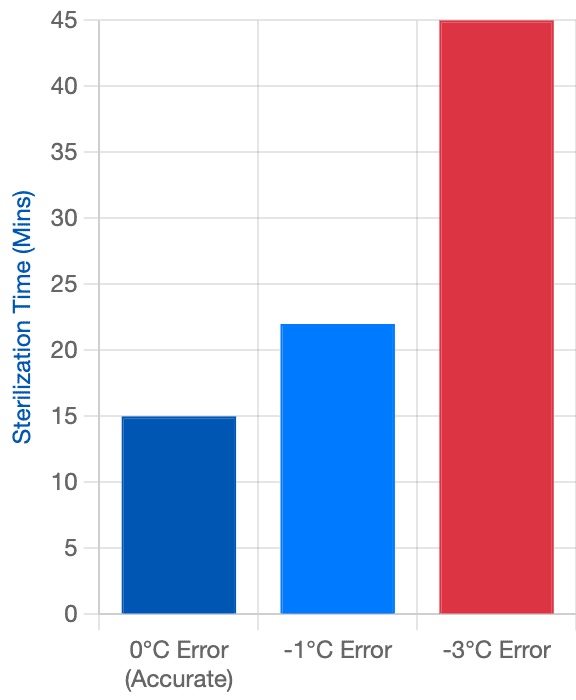
Temperature Error = Time Loss
Even 1°C error significantly increases the sterilization cycle.
Benefits (🟢) vs. Risks (🔴)
BENEFITS (CALIBRATION)
- ✅ Patient Safety (Low HAIs)
- ✅ Regulatory Compliance (FDA/GMP)
- ✅ Increased Efficiency (Energy Savings)
RISKS (NO CALIBRATION)
- ❌ Non-Sterile Products
- ⚠️ Fines / Operational Suspension
- 💰 Wasted Energy & Costs
2.1. Guaranteeing Absolute Biological Efficacy
Calibration confirms that the actual temperature and pressure inside the chamber match the values shown on the control panel.
- Temperature Control: Standard sterilization temperature usually is (for 15 minutes) or (for 3 minutes). Consider this: If the autoclave’s temperature sensor is wrong by just a few degrees (it shows but only reaches ), the sterilization will fail. Therefore, heat-resistant bacterial spores will survive. Calibration finds and fixes this error.
- Temperature Mapping and Uniformity: Further, advanced calibration includes Temperature Mapping. Technicians place multiple reference sensors (calibrated PRTs or Thermocouples) in many spots inside the chamber. They do this to find any “cold spots” where steam cannot reach properly. This ensures heat spreads evenly across the entire load.
- Pressure Verification: Pressure (usually or above air pressure) is needed to keep water as saturated steam at the required heat. Calibration of the pressure gauge confirms this reading is correct.
2.2. Protecting Tools and Property
- Preventing Device Damage: If the real temperature is higher than the displayed temperature, sensitive tools, medical plastics, or heat-sensitive materials can melt, bend, or break. This results in high replacement costs. Importantly, calibration keeps the temperature within safe limits.
2.3. Legal Compliance and Quality Assurance
In the medical and drug industries, laws mandate calibration for quality control.
- Proving Validation: A Calibration Certificate from an ISO/IEC 17025 accredited lab offers solid proof. It proves the facility followed the right steps and the equipment performs to national/international standards (like FDA, cGMP, and ISO rules).
- Staying Ready for Audits: When quality auditors (such as JCI or local health groups) inspect a facility, complete and correct autoclave calibration records are vital. They need this information to keep their operating license.
3. How Autoclave Calibration Works
Calibrating an autoclave is a complex technical process. Specialists carry out this work:
- Setting up Standards: The technician places reference temperature and pressure sensors (which trace back to national standards) at key spots inside the chamber.
- Running the Cycle: Technicians run one or more typical sterilization cycles (e.g., ).
- Collecting Data: An external data recorder captures the actual temperature and pressure from the reference sensors throughout the cycle.
- Checking and Fixing: Experts check the data against the set rules and allowed error limits. If the error is too high, the technician adjusts the autoclave’s built-in sensors.
- Giving the Certificate: Finally, the lab issues a detailed Calibration Certificate. This officially confirms the autoclave meets the necessary sterilization standards.
Conclusion
The Autoclave provides the core foundation of biological safety in all sensitive areas. It is used everywhere, from saving lives in the operating room to protecting the data in important research. However, we only keep the autoclave’s power active through regular Calibration. Calibration is not just a technical step; it is a required investment. It helps remove the risk of infection, protect expensive medical property, and keep the facility legally compliant. By making sure truly is , we maintain our promise of absolute safety and quality.
Have you checked your facility’s last Autoclave calibration date?



