Calibration of Multifunction Testers: Ensuring Absolute Safety for EV Charging Stations (EVSEs)
The electric vehicle revolution is gaining incredible momentum. As millions of zero-emission vehicles hit the road, an essential infrastructure is rapidly developing alongside them: electric vehicle charging stations (EVSEs). However, these power-delivery devices are more than just large electrical outlets. They are complex electrical systems that operate at high power levels. We must ensure the safety of these charging stations, and the key lies in the hands of electrical engineers who use a calibrated tool: the installation multifunction tester.
Calibration of multifunction testers is a highly specialized technical process, yet it is the very foundation of safety. You cannot skip this step. Calibration guarantees that every measurement is accurate, thereby confirming that each charging station is unequivocally safe. This article will show you the critical importance of calibration in the installation and maintenance of EVSEs. We will also highlight why it is a vital factor for businesses in this industry.
The EV Charging Station: More Than an Outlet

An EVSE is far more complex than a standard residential electrical outlet. It not only transfers power but also continuously communicates with the vehicle to determine the appropriate charging rate. Since they operate at high power, charging stations pose serious risks if technicians do not install them correctly. These risks include:
- Risk of Electric Shock: High currents can be lethally dangerous if a fault occurs.
- Risk of Fire: Substandard wiring and equipment can overheat and ignite, causing a fire.
- Damage to the EV Battery: A minor electrical fault can cause significant damage to the vehicle’s battery pack, which is its most expensive component.
Therefore, every charging station requires a meticulous test and certification. You cannot perform this with visual inspection alone; it requires specialized measuring tools.
The Importance of MFTs
Multifunction Testers (MFTs) are essential tools for safety and performance checks of electric vehicle charging stations (EVSEs). They measure critical parameters such as loop impedance, insulation resistance, and RCD/RCBO trip times.
Regular calibration of MFTs is mandatory to ensure accurate measurements, thereby protecting users, vehicles, and the electrical infrastructure.
MFT Market Share
The Critical Role of Calibration in EVSE Safety
An installation multifunction tester is the central tool in this process. It can perform a variety of measurements, such as insulation resistance, earth resistance, and the function of Residual Current Devices (RCDs). However, an uncalibrated tester is like a clock that tells the wrong time. Its results have no value and can lead to catastrophic consequences.
What is Calibration?
Calibration is a process where technicians compare a measuring device to a certified standard to verify and adjust its accuracy. For a multifunction tester, this ensures that every measurement it takes is reliable and can be trusted.
Key Measurements That Require Calibration:
- RCD Testing: The RCD is the primary protective “brain.” It trips the circuit instantly upon detecting a current leakage. A calibrated tester ensures the RCD operates within the correct time and current thresholds, protecting the user from the risk of electric shock.
- Loop Impedance Measurement: This test determines if the short-circuit current is large enough to activate a fuse or breaker. An inaccurate value could lead to a situation where the protective device fails to trip, resulting in a fire hazard.
- Ground Resistance Testing: The grounding system is the final line of defense. The calibration of the tester ensures that the earth resistance is low enough to safely dissipate a fault current into the ground, protecting both the user and the equipment.
Installation and Testing According to Standards
The calibration of a multifunction tester is an indispensable part of an installation and maintenance process that complies with international standards like IEC 60364 (Electrical installations for buildings). This process typically includes the following steps:
- System Installation: Engineers install the EVSE along with all associated protective devices (RCD, fuses, breakers).
- Initial Testing: They use a calibrated multifunction tester to perform a series of safety measurements according to the required standards. This is the most crucial step to confirm that the installation is correct and safe.
- Certification Generation: After the tests pass, a report or certificate is generated. This report must include the measurement results and confirm that engineers tested the equipment using a calibrated tool.
- Periodic Maintenance: Technicians inspect charging stations regularly to ensure they remain safe to operate. They need to re-calibrate the tester on a regular schedule (often annually) to ensure the reliability of maintenance reports.
Business Benefits and Customer Trust
In a rapidly growing market like electric vehicles, building trust is a key differentiator. Using a calibrated tester gives businesses numerous significant advantages:
- Legal Compliance: It ensures your business meets all electrical safety regulations, helping you avoid legal risks and administrative fines.
- Risk Mitigation: It minimizes the risk of electrical faults, protects assets, and helps you avoid costly liability claims.
- Building Customer Trust: When users see that a rigorous process has certified your charging station as safe, they feel more secure using it. This helps you build a solid reputation for quality and reliability.
Risks of Skipping Calibration
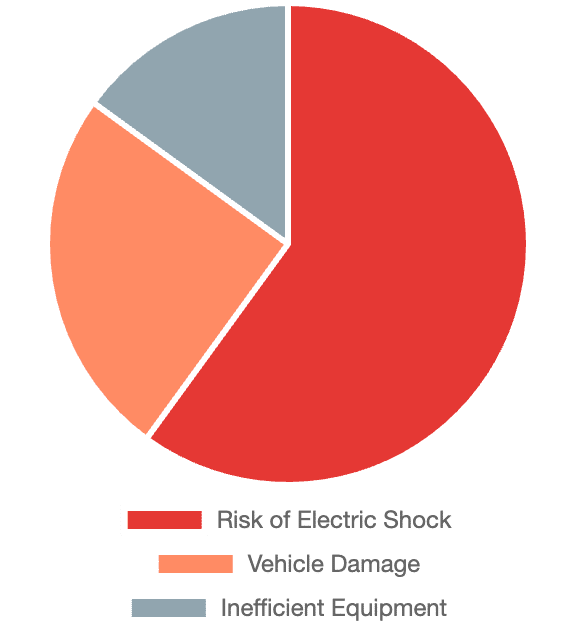
Potential Failures
- ✗
Risk of Electric Shock: Due to protective devices like RCDs not functioning.
- ✗
Vehicle Damage: Unstable current can damage the EV battery.
- ✗
Financial Loss: Due to inefficient charging equipment or costly repairs.