In high-voltage testing environments, accuracy and safety are non-negotiable. Hipot Testers (High Potential Testers) are essential tools for verifying insulation integrity and preventing electrical hazards in industrial systems. These instruments apply a high test voltage between conductors and ground to check whether current leakage stays within safe limits.
However, even minor deviations in measurement or output voltage can lead to false results, non-compliance, or safety risks. That’s why regular Hipot Tester Calibration is a crucial part of every electrical safety program — ensuring your testers perform precisely as intended, every single time.

Why Calibration is Non-Negotiable
A Hipot Tester’s role is to push equipment to its voltage withstand limit — but if its readings drift, the entire safety assurance chain collapses.
Here’s why calibration isn’t just optional maintenance:
-
Accuracy: Confirms test voltage and leakage current readings remain within specified tolerances.
-
Compliance: Aligns results with standards such as IEC 61010, IEC 60950, and ISO/IEC 17025.
-
Safety: Protects operators, end-users, and connected devices from unnoticed insulation failures.
The Economics of Accuracy
An uncalibrated Hipot tester is a hidden liability. The financial consequences of a single missed insulation failure can far outweigh the preventative cost of routine calibration.
Includes logistics, replacement units, and brand damage from safety failures.
A minor operational expense with major risk reduction ROI.
The Inevitable Drift
Without regular calibration, every tester’s performance degrades. Electronic components age and environmental factors cause a gradual “drift” from the manufacturer’s specifications, leading to inaccurate readings.
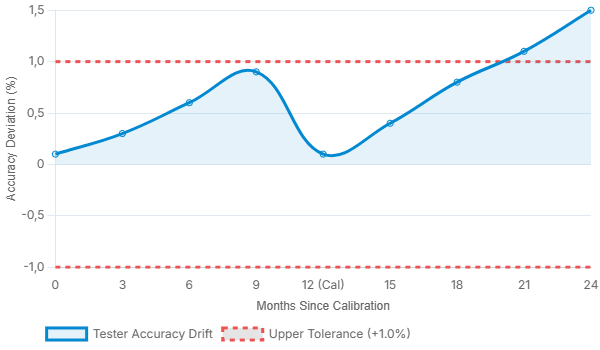
This chart illustrates how a tester’s voltage output accuracy can drift outside of acceptable tolerance levels over 24 months if left uncalibrated.
Primary Drivers for Hipot Tester Calibration
Regular calibration provides measurable value across multiple aspects of electrical testing operations:
-
Verification of Test Voltage Output – Ensures the applied high voltage matches display values under both AC and DC modes.
-
Leakage Current Accuracy – Confirms that low current measurements (typically in µA range) remain stable and traceable.
-
Traceability to National Standards – Links each measurement to recognized metrological institutions.
-
Preventive Maintenance – Detects internal drift, damaged probes, or insulation degradation before costly failures occur.
-
Regulatory & Audit Readiness – Supports documentation for ISO/IEC 17025, GMP, or internal quality systems.
Ensure your Hipot Testers deliver reliable, compliant performance.
Contact Techmaster Vietnam for accredited Hipot Tester Calibration — trusted by leading manufacturers across the region.
The Calibration Lifecycle
A professional Hipot Tester calibration process typically follows four key stages:
-
Pre-Check & Functional Inspection
Visual examination of cables, probes, and display indicators to identify signs of damage or wear. -
Voltage Output Verification
The Hipot Tester is connected to a high-voltage reference meter to compare indicated and actual voltages across multiple test points. -
Leakage Current Measurement
Measured leakage current values are verified using precision ammeters at both low and high voltage levels. -
Adjustment & Documentation
If deviations exceed tolerance limits, the technician adjusts internal parameters. A final ISO/IEC 17025 traceable certificate is then issued.
Each step ensures that the tester’s output remains reliable and consistent with national and international standards.
The Gold Standard: ISO/IEC 17025 Calibration
Calibration without accreditation may provide data, but not assurance.
That’s why Techmaster’s laboratories operate under ISO/IEC 17025 — the global benchmark for calibration competence.
This certification ensures that every Hipot Tester calibration performed by Techmaster is:
-
Traceable to national metrology institutes (NMI);
-
Verified through periodic proficiency testing;
-
Conducted by trained engineers using certified reference standards;
-
Documented with uncertainty analysis and test conditions.
With ISO/IEC 17025 compliance, your audit trail remains airtight, and your test results — defensible.
Calibrated vs. Uncalibrated: The Real-World Impact
The data is clear. Production lines using properly calibrated Hipot testers consistently exhibit lower rates of post-shipment electrical failures, preventing recalls and protecting consumers.
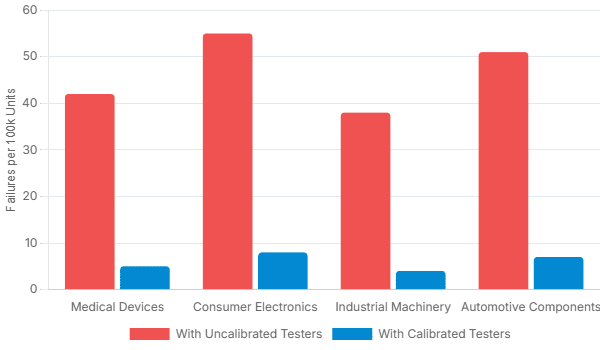
Comparison of failure rates per 100,000 units shipped, based on whether the production line’s Hipot testing equipment was within its calibration cycle.
Recommended Calibration Frequency
How often should a Hipot Tester be calibrated?
That depends on how intensively it’s used and the operating environment.
| Usage Level | Recommended Interval | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Standard laboratory / moderate use | Every 12 months | Industry standard interval |
| High-usage / production line | Every 6 months | Prevents drift from heavy use |
| Harsh environments (dust, humidity, vibration) | Every 3–6 months | Proactive maintenance recommended |
Regular calibration prevents undetected drift and maintains consistency across multiple testing stations.
Choosing the Right Calibration Provider
Not all calibration services are created equal. When selecting a lab for your Hipot Tester, look for these essential qualifications:
-
ISO/IEC 17025 accreditation specifically covering high-voltage calibration.
-
Experience with multiple Hipot Tester brands (Chroma, GW Instek, Fluke, Kikusui, etc.).
-
Ability to provide Before–After calibration data for transparency.
-
Fast turnaround and local support to minimize downtime.
-
Professional reporting with clear uncertainty statements.
Case Study: Chroma 19073 Hipot Tester Calibration
One of the most common models serviced by Techmaster is the Chroma 19073, used widely in electronics manufacturing and quality assurance.
Recently, a client operating a high-volume test line noticed inconsistent pass/fail results during dielectric withstand tests. After calibration by Techmaster, the Chroma 19073 was found to have a voltage output deviation of +1.8% — outside the manufacturer’s specification of ±1%.
Techmaster engineers:
-
Identified drift in the high-voltage module,
-
Adjusted internal calibration constants,
-
Verified leakage current measurement accuracy, and
-
Issued an updated calibration certificate with traceable results.
The outcome?
The client restored test reliability, improved production yield, and passed its ISO/IEC 17025 audit seamlessly.
Have you tested your Hipot’s accuracy lately?
Schedule a traceable calibration with Techmaster to prevent downtime and audit surprises.
Techmaster’s Calibration Capability
Techmaster Vietnam is one of the country’s leading providers of electrical and electronic calibration services, trusted by manufacturers, laboratories, and R&D centers nationwide.
Our High-Voltage Calibration Lab offers:
-
Calibration up to 10 kV AC/DC with high-precision reference meters.
-
Accredited under ISO/IEC 17025 by the Bureau of Accreditation (BoA).
-
Trained engineers with over 15 years of field experience.
-
Nationwide pickup and delivery service for convenience.
-
Digital certificates and result archives for easy compliance management.
Techmaster’s expertise covers multiple categories, including Hipot Testers, Ground Bond Testers, Insulation Resistance Testers, and Electrical Safety Analyzers.
Conclusion: Safety Starts with Precision
A Hipot Tester is only as trustworthy as its calibration.
By ensuring precise voltage and current readings, you’re not just meeting compliance standards — you’re safeguarding lives, equipment, and your company’s reputation.
Don’t let drift go unnoticed.
Trust Techmaster to keep your electrical safety instruments performing at their best.



