Digital Refrigerant Scale: Ensuring Optimal HVAC/R System Performance – The Absolute Necessity of Calibration

In the HVAC/R industry (Heating, Ventilation, Air Conditioning, and Refrigeration), the amount of refrigerant charged into a system critically determines its performance, lifespan, and energy efficiency. Indeed, overcharging with refrigerant can damage the compressor and waste energy. Conversely, undercharging prevents the system from reaching the required temperature, ultimately reducing cooling efficiency and stressing the equipment. The Digital Refrigerant Scale is an indispensable tool for every professional HVAC/R technician. Specifically, this device allows them to precisely measure the refrigerant amount added to or recovered from a system. However, because electronic scales are highly sensitive mass measuring instruments and frequently bear heavy loads, periodic Refrigerant Scale Calibration becomes a mandatory requirement. Calibration verifies the scale’s accuracy. Consequently, it ensures that refrigerant charging always adheres to stringent manufacturer specifications, thereby optimizing performance and protecting the environment.
1. What is a Digital Refrigerant Scale?
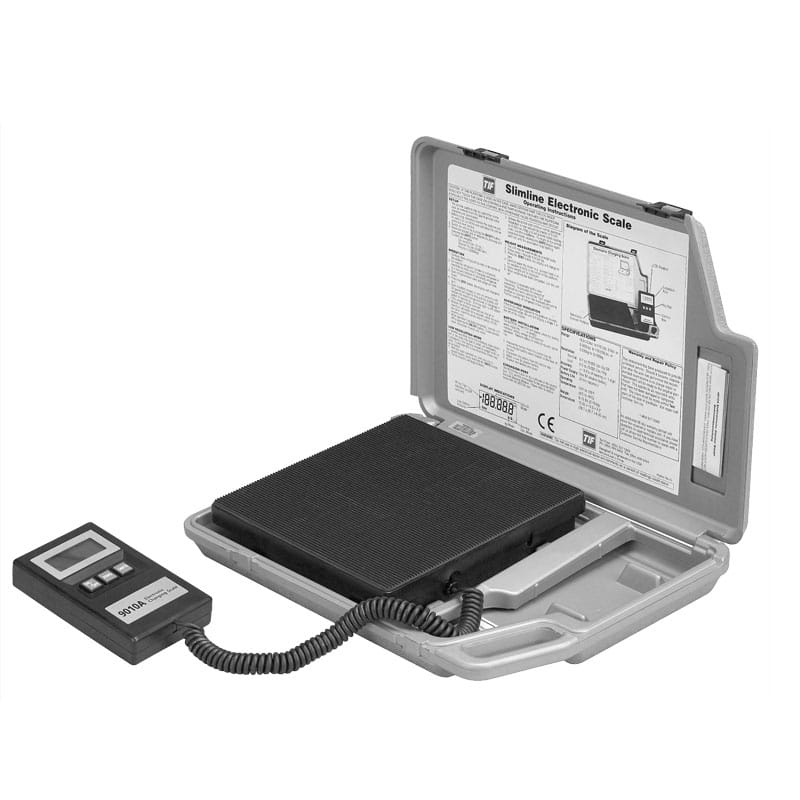

A Digital Refrigerant Scale is a specialized mass measuring device. We design it to accurately determine the weight of the refrigerant in a cylinder during charging or recovery operations.
Impact of Refrigerant Charge on System Performance
Visual representation of performance at different charge levels.
1.1. Objective and Key Measurement Functions
-
Objective: The goal is to ensure the precise amount of refrigerant charged into the system. This must strictly follow the equipment manufacturer’s specifications (often in grams or ounces).
-
Key Measurement Functions:
-
Mass Measurement: It determines the refrigerant remaining in the cylinder or the exact amount of refrigerant added/recovered.
-
Tare/Zero Function: Furthermore, this feature allows the technician to reset the zero point after placing the refrigerant cylinder on the scale, measuring only the refrigerant that moves.
-
High Resolution: Crucially, it offers the necessary accuracy (typically ± 0.5%) to meet system technical requirements.
-
1.2. Basic Operating Principle
Refrigerant Scale Operating Principle
The scale uses a Load Cell sensor to convert force into an electrical signal, which is then processed and displayed.
Load Cell Sensor
Converts force into voltage signal
Signal Processor
Converts voltage into mass unit
Digital Display
Shows final measurement
-
Load Cell: The scale uses one or more load cells (typically Strain Gauge type). In essence, this sensor converts the force (weight) applied to the platform into a proportional electrical signal.
-
Signal Processor: The electrical signal from the load cell is processed, amplified, and converted into mass units (e.g., kg, g, oz, lb) via an internal algorithm.
-
Digital Display: Finally, the results are clearly displayed on a digital screen, which allows the technician to easily monitor the refrigerant amount.
2. Vital Applications in HVAC/R and Environmental Protection
The ability to accurately measure refrigerant mass is a key factor. Certainly, it directly affects system performance and environmental impact.
2.1. Air Conditioning System Installation and Maintenance
-
Optimal Charging: This remains the core application. After installation or repair, technicians must charge the precise amount of refrigerant based on design specifications. Therefore, an inaccurate scale can easily lead to an overcharged or undercharged system.
-
Leak Detection: During maintenance, the scale helps accurately determine the remaining refrigerant mass in the system. Comparing this value with the specifications quickly assesses the severity of a leak.
2.2. Industrial and Commercial Refrigeration
Large Refrigeration Systems: Refrigeration systems for warehouses, supermarkets, and factories require large amounts of refrigerant. Consequently, we must charge these systems with extreme accuracy to maintain stable temperatures, preventing product spoilage.
2.3. Environmental Compliance and Refrigerant Recovery
Refrigerant Recovery: When repairing or decommissioning old systems, technicians must recover the refrigerant into recovery cylinders. In this context, the Refrigerant Charging Scale helps accurately measure the recovered amount. This ensures compliance with environmental regulations (e.g., Montreal Protocol) and hazardous waste management rules.
3. The Absolute Role of Refrigerant Scale Calibration
Why Calibration Matters
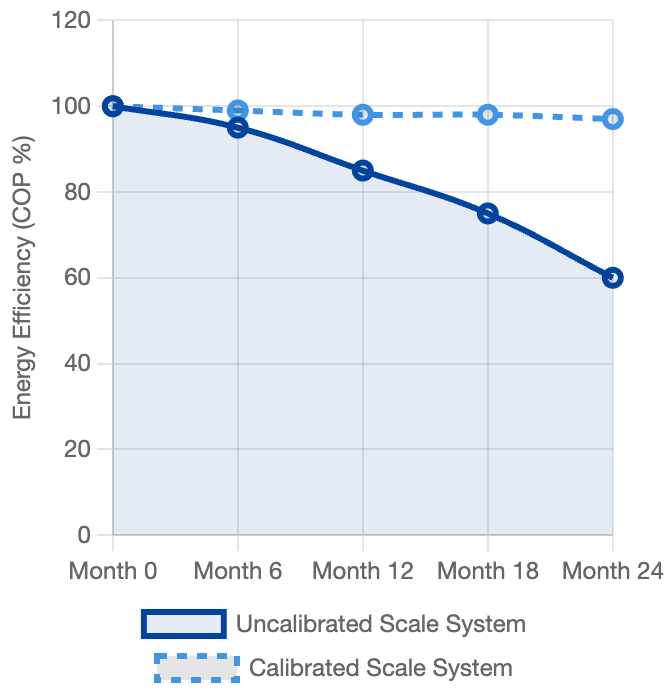
Load Cell sensors drift over time due to usage, impact, and aging. Calibration prevents inaccurate refrigerant charge.
System Efficiency (COP) Drop Due to Scale Error
Comparison of Mass Error Margin
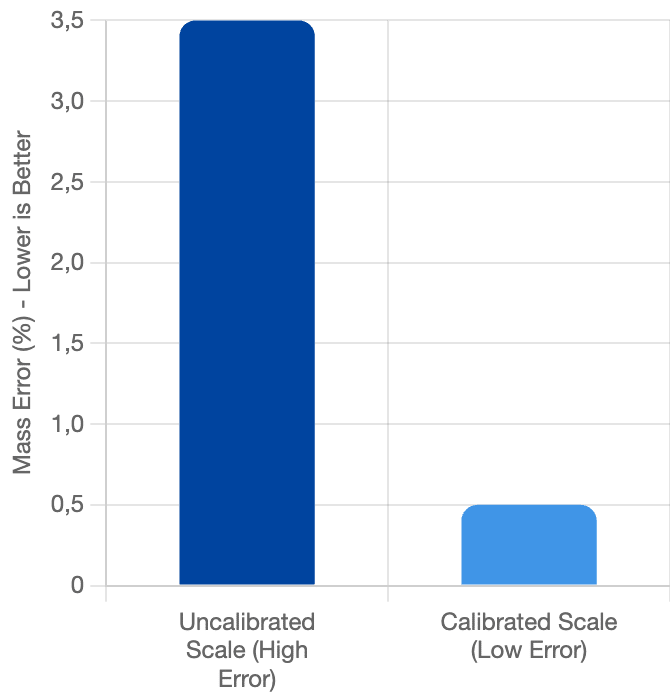
An inaccurate refrigerant mass measurement can cause energy waste, equipment damage, and environmental legal violations. Therefore, this risk makes Refrigerant Charging Scale Calibration paramount.
3.1. Ensuring Optimal Performance and Technical Compliance
-
Risk of Accuracy Degradation (Drift): The load cell of an electronic scale can drift, become misaligned, or suffer minor damage due to impact or continuous load bearing. Such inaccuracy results in over- or under-charging the refrigerant.
-
Optimizing Efficiency: Refrigerant Charging Scale Calibration verifies that the scale measures mass accurately. This, in turn, ensures technicians charge the correct refrigerant amount, helping the system achieve optimal cooling performance and extending the compressor lifespan.
-
Value Verification: Ultimately, calibration confirms that the displayed mass value matches the actual mass, based on reference mass standards.
3.2. Legal Compliance and Safety Audits
-
Standard Requirements: HVAC/R industry regulations and standards mandate that an ISO/IEC 17025 accredited laboratory must periodically calibrate critical mass measuring equipment.
-
Environmental Evidence: During refrigerant recovery, accurate data from the scale serves as evidence of compliance with environmental regulations. Thus, the Calibration Certificate proves this data is reliable.
4. Refrigerant Charging Scale Calibration Process
Calibration Procedure (ISO/IEC 17025)
Reference Weights
Multi-Point Check
Adjustments
Certification
The process of Refrigerant Charging Scale Calibration requires standard equipment and strict procedures.
-
Reference Weights: Technicians use high-precision, traceable, and calibrated standard test weights (often F1, F2 class weights).
-
Check and Compare: A technician places the standard test weights onto the refrigerant charging scale at multiple load points (from low load to maximum capacity). Then, they compare the mass value displayed on the scale with the precise known mass value of the standard weight.
-
Adjustment (if necessary): If a deviation beyond set limits occurs, the scale is adjusted (linearization) to match the standard value across its measuring range.
-
Certification: Following the check, a Calibration Certificate is issued, confirming the scale’s accuracy and the next calibration due date.
Conclusion
The Digital Refrigerant Scale is the foundation of all professional HVAC/R installation and maintenance work. Crucially, however, for the work to achieve optimal performance and comply with strict regulations, the scale’s accuracy must be guaranteed. Periodic Refrigerant Scale Calibration is a mandatory procedure that technicians cannot overlook. Therefore, it ensures technicians always charge the correct amount of refrigerant, helping systems operate efficiently, save energy, and contribute to sustainable environmental protection.